|
|
|
Six cancer
patients suffering from pickle cell carcinoma of esophagus, malignant melanoma, liver
cancer, malignant lymphoma, bladder cancer and breast cancer. Six control
patients with hepatitis (14a), chr. tonsillitis (41a), M. Parkinson (78a),
healthy (12a), healthy (14a), healthy (20a). For the diagnoses and the material
I have to thank R.Pekar.
(M =
maceration, F = filtration)
Between the
groups of cancer patients and the control group the following differences
became evident: In the blood of a
cancer patient 21.917 +/- 913 particles per µl were found (17.444 –
26.389; n=6). In the control group 1220 +/- 478 particles per µl blood were counted (0 – 3358 ;
n=6). After the t-test a significant difference - admitting an error
probability of 5% - was found. The difference becomes clear in fig.1 compared
with fig. 2a and 2b. Also nano – colonies of these particles ( fig. 3a) like a
corncob could be detected. In fig. 3b one can see a nano – colony with small
crystales between the particles.
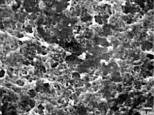
Fig.1 Particles
of a healthy person (12a, male) in SEM, magnification 6250 : 1
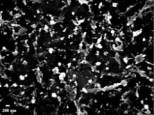
Fig. 2a
Particles (Basoplasma sanguineum) of
a cancer-patient (liver-cancer, male) in SEM, magnification 6250 : 1. ( higher resolution)
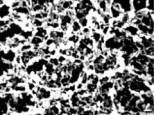
Fig. 2b Particles
(Basoplasma sanguineum) of a
cancer-patient (breast-cancer, 44a) in SEM, magnification 6250 : 1
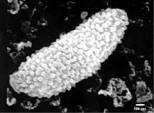
Fig. 3a
Nano-colony of particles (Basoplasma
sanguineum), prickle cell carcinoma of esophagus in SEM, magnification 6250 : 1. (higher
resolution)

Fig. 3b
Nano-colony of particles (Basoplasma
sanguineum), prickle cell carcinoma of esophagus in SEM, magnification 6250 : 1. (higher
resolution)
Preface Introduction
Blood Analyses Culture
Immunfluorescence Animal
Experiment Discussion Summary Literature Biography